Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions

Ever wonder what happens to your used data center equipment after decommissioning? There’s an entire industry set up to recover value from used equipment and maximize resource recovery, either through reuse or responsible recycling. This industry is known as the IT asset disposition (ITAD) and e-waste recycling industry.
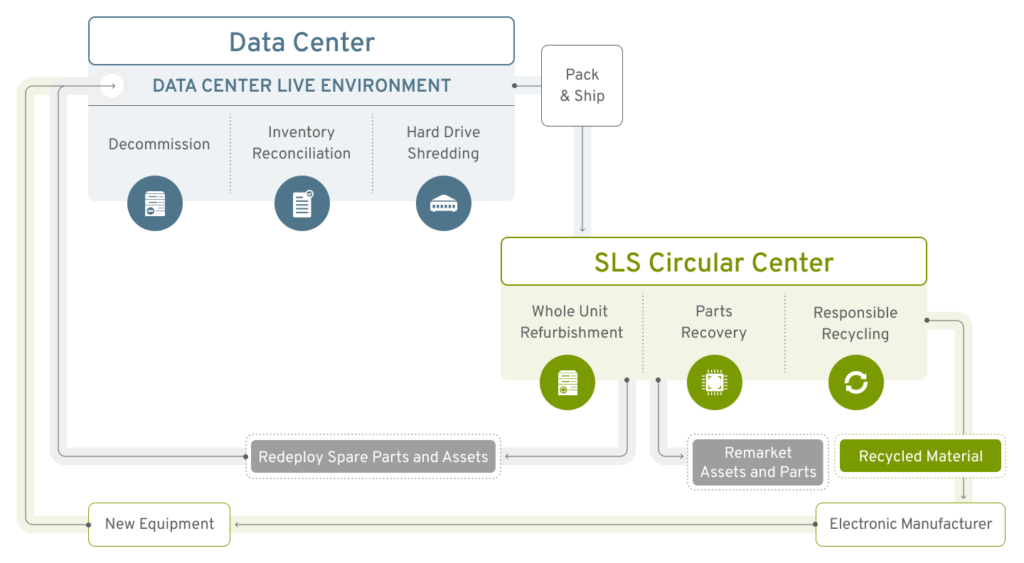
Equipment is shipped to an ITAD facility specializing in handling data center equipment. These processing facilities are set up to triage equipment systematically, destroy data and prepare equipment for reuse or recycling. Some ITAD facilities handle reuse and recycling. Other facilities handle reuse and will send obsolete hardware and e-waste to a separate facility for recycling. Most commonly housed in an industrial warehouse, there are areas within the ITAD facility dedicated to performing specific tasks. These sites have taken on added importance as companies seek to reduce their carbon impact. Reusing and recycling data center equipment contributes to the circular economy and improves financial results.
When received at the ITAD facility, an electronic inventory of assets is typically done and confirmed with your organization. At a minimum, asset make, model and serial number is captured. This information becomes part of an electronic chain of custody record to confirm secure and compliant handling of the IT assets.
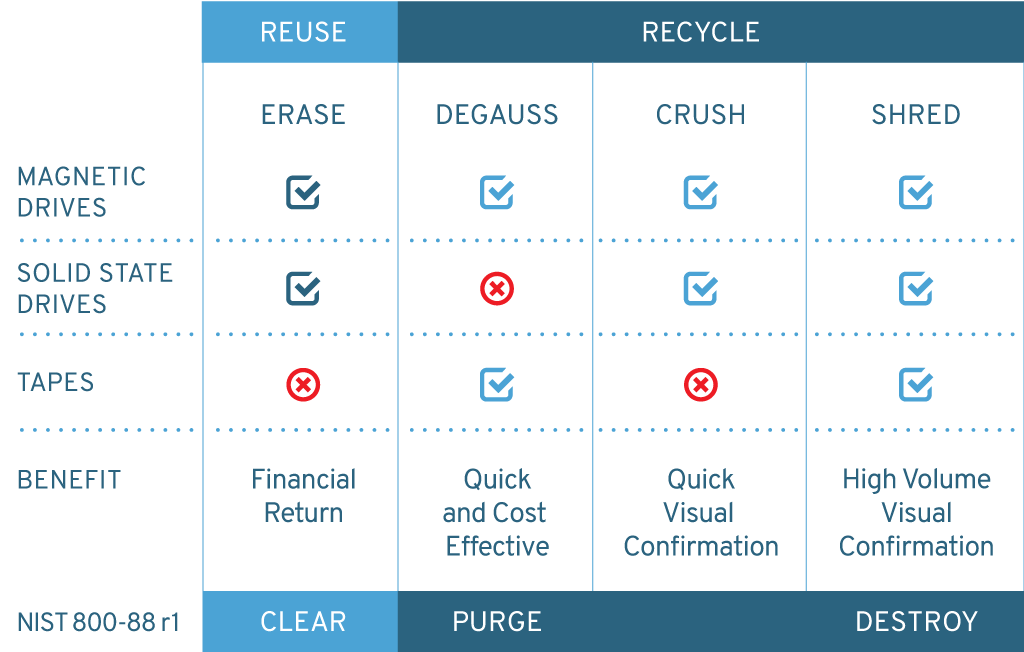
Data is destroyed by data erasure, shredding, crushing or degaussing of storage media. As shown in the chart, data erasure allows secure reuse of storage devices. Magnetic hard drives and magnetic tapes, solid state drives and optical storage devices each require different data destruction methods. Certificates of Data Destruction (CODD) are provided by the vendor during the project. The CODD demonstrates compliance to corporate and regulatory requirements, including the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
Data center equipment can be reconfigured and refurbished and then redeployed to another company owned data center. If whole units cannot be reused, spare part recovery can be a smart option to maintain legacy equipment. Redeployment of whole units and parts is a great way to conserve resources, save money and reduce the carbon impact of your IT ecosystem.
If there is no internal need for the decommissioned equipment, it can be resold on your behalf. Equipment condition and age of equipment is evaluated, to determine whether equipment will be reused or recycled. These behind-the-scenes activities help offset the cost of decommissioning, data destruction, shipping and reporting.
See how equipment is sold.
A parts recovery program provides an additional revenue source when assets cannot be sold as a whole unit.
Any equipment that is obsolete or beyond economical repair is recycled. The recycling process separates steel, plastic, aluminum, copper and precious metals from each other, which then allows for reuse of these commodities in next generation products.
Once resold, recycled or redeployed, reporting helps document an audit trail for the final disposition of all assets. Asset reporting should include detailed asset information, final disposition, pricing, and dates of significant activities. You should have the ability to receive data feeds or view online reports and be able to download .csv through a portal, which might include Certificates of Data Destruction, Certificates of Recycling and Certificates of Sustainability.

SLS engages collaboratively with global clients to re-examine business models and to plan for continual evolution towards a circular economy model. Clients leverage our knowledge about disposition of retired electronic assets, managing their movement through reverse supply chains, and quantifying the carbon impact of these assets.